Chlorine sensors
To measure chlorine concentration we offer sensors CSCT 43-R and CSUT 43-R.
Both sensors are membrane diffusion sensors intended for the measurement of chlorine concentration in water. Temperature is measured simultaneously.
The chlorine section of the sensor is made up of polarizing electrode - a cathode and non-polarizing argent chloride electrode. Both electrodes are submerged in electrolyte and separated from the measured medium by a separating membrane, which is chlorine permeable, (also permeable to other gases - O2, O3, ClO2, CO2).
By the application of a suitable voltage between the electrodes chlorine (hypochlorous acid, hypochlorite ion) reduction occurs on the cathode surface. The result of this reaction is an electric current between the sensor electrodes, which is proportional to the concentration of HOCl at the CSCT 43-R sensor and HOCl + OCl- at the CSUT 43-R.
Chlorine sensors (when active) consume chlorine, which is removed from the measured medium. Therefore all factors which influence the speed of diffusion toward the cathode surface are applied during measurement.
Sensor current is influenced by temperature. Temperature dependence is exponential and has to be compensated for in the controller. In order to make high quality compensation in both sensors a temperature sensor has been integrated.
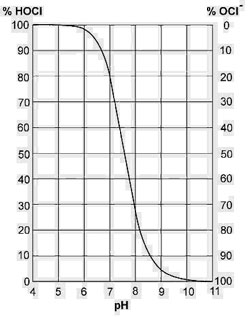
When chlorine gas is dissolved in water (or bleach is added), hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite ion (OCl) are generated, which are at a mutual standstill controlled by the pH value. As long as ammonia ions are present in water, chloramines are also generated. Hypochlorous acid is an efficient disinfectant. Its disinfecting power is 20 to 100 times higher than that disinfecting power of hypochlorite ion. The CSCT sensor measures the concentration of hypochlorous acid. Its signal is approximately to pH 5.0 independent of the pH value. At higher pH value the sensor signal decreases according to the distribution curve mentioned below.
With free chlorine evaluation by DPD method, elementary chlorine, hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ion is determined. This value is higher than the value obtained from the CSCT 43-R sensor – signal of the sensor is proportional to free active chorine (elementary chlorine + hypochlorous acid). The output signal of the CSUT 43-R sensor is proportional to the concentration of elementary chlorine, hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ion so that consequently to the free chlorine.
Percent Fraction of Hypochlorous Acid and Hypochlorite vs. Solution pH
From the above mentioned results we see that the CSCT 43-R is an ideal sensor for chlorine measurement and control, where it is necessary to measure the actual disinfecting efficiency of the chemicals dosed, meaning the concentration of hypochlorous acid. A great advantage is the measurement independence for the presence of other substances in water, the undemanding attendance and the resistance to pollution.
The CSUT 43-R sensor is suitable for use where it is necessary to measure the free chlorine volume and pH value varies.
Sensors Specifications
| CSCT 43-R | |
|---|---|
| Sensor Type | polarographic membrane sensor |
| Sensor Signal | the signal is proportional to partial pressure of chlorine and hypochlorous acid - it means the signal is proportional to the disinfecting efficiency of the disinfecting substance, and the signal depends on the pH value |
| Measurement Range | 0,01 to 5,0 mg/l |
| Fluctuation of the Zero Signal | ±0,02 mg/l |
| Temperature Compensation | built in, thermistor NTC |
| Response Time (25°C) | t90 - 120s (chlor) |
| Temperature Range | 1 to 40°C |
| pH Range | 4 to 8,4 pH units |
| Minimum Flow Rate | 20 cm/s |
| CSUT 43-R | |
| Sensor Type | polarographic membrane sensor |
| Sensor Signal | the signal is proportional to free chlorine concentration |
| Measurement Range | 0,01 to 6,0 mg/l |
| Fluctuation of the Zero Signal | ±0,05 mg/l |
| Temperature Compensation | built in, thermistor NTC |
| Temperature Range | 1 to 40°C |
| pH Range | 5,5 to 9,0 pH units |
| Minimum Flow Rate | 4 cm/s (03,l/min in PB unit) |




